Walrus is a distributed message streaming platform built on a high-performance log storage engine. It provides fault-tolerant streaming with automatic leadership rotation, segment-based partitioning, and Raft consensus for metadata coordination.
Key Features:
- Automatic load balancing via segment-based leadership rotation
- Fault tolerance through Raft consensus (3+ nodes)
- Simple client protocol (connect to any node, auto-forwarding)
- Sealed segments for historical reads from any replica
- High-performance storage with io_uring on Linux
Producers and consumers connect to any node (or via load balancer). The cluster automatically routes requests to the appropriate leader and manages segment rollovers for load distribution.
Each node contains four key components: Node Controller (routing and lease management), Raft Engine (consensus for metadata), Cluster Metadata (replicated state), and Bucket Storage (Walrus engine with write fencing).
Node Controller
- Routes client requests to appropriate segment leaders
- Manages write leases (synced from cluster metadata every 100ms)
- Tracks logical offsets for rollover detection
- Forwards operations to remote leaders when needed
Raft Engine (Octopii)
- Maintains Raft consensus for metadata changes only (not data!)
- Handles leader election and log replication
- Syncs metadata across all nodes via AppendEntries RPCs
Cluster Metadata (Raft State Machine)
- Stores topic → segment → leader mappings
- Tracks sealed segments and their entry counts
- Maintains node addresses for routing
- Replicated identically across all nodes
Storage Engine
- Wraps Walrus engine with lease-based write fencing
- Only accepts writes if node holds lease for that segment
- Stores actual data in WAL files on disk
- Serves reads from any segment (sealed or active)
cd distributed-walrus make cluster-bootstrap # Interact via CLI cargo run --bin walrus-cli -- --addr 127.0.0.1:9091 # In the CLI: # create a topic named 'logs' > REGISTER logs # produce a message to the topic > PUT logs "hello world" # consume message from topic > GET logs # get the segment states of the topic > STATE logs # get cluster state > METRICS
Simple length-prefixed text protocol over TCP:
Wire format:
[4 bytes: length (little-endian)] [UTF-8 command]
Commands:
REGISTER <topic> → Create topic if missing
PUT <topic> <payload> → Append to topic
GET <topic> → Read next entry (shared cursor)
STATE <topic> → Get topic metadata (JSON)
METRICS → Get Raft metrics (JSON)
Responses:
OK [payload] → Success
EMPTY → No data available (GET only)
ERR <message> → Error
See distributed-walrus/docs/cli.md for detailed CLI usage.
- Topics split into segments (~1M entries each by default)
- Each segment has a leader node that handles writes
- Leadership rotates round-robin on segment rollover
- Automatic load distribution across cluster
- Only the leader for a segment can write to it
- Leases derived from Raft-replicated metadata
- 100ms sync loop ensures lease consistency
- Prevents split-brain writes during leadership changes
- Old segments "sealed" when rolled over
- Original leader retains sealed data for reads
- Reads can be served from any replica with the data
- No data movement required during rollover
- Monitor loop (10s) checks segment sizes
- Triggers rollover when threshold exceeded
- Proposes metadata change via Raft
- Leader transfer happens automatically
| Flag | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
--node-id |
(required) | Unique node identifier |
--data-dir |
./data |
Root directory for storage |
--raft-port |
6000 |
Raft/Internal RPC port |
--raft-host |
127.0.0.1 |
Raft bind address |
--raft-advertise-host |
(raft-host) | Advertised Raft address |
--client-port |
8080 |
Client TCP port |
--client-host |
127.0.0.1 |
Client bind address |
--join |
- | Address of existing node to join |
| Variable | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
WALRUS_MAX_SEGMENT_ENTRIES |
1000000 |
Entries before rollover |
WALRUS_MONITOR_CHECK_MS |
10000 |
Monitor loop interval |
WALRUS_DISABLE_IO_URING |
- | Use mmap instead of io_uring |
RUST_LOG |
info |
Log level (debug, info, warn) |
Comprehensive test suite included:
cd distributed-walrus # Run all tests make test # Individual tests make cluster-test-logs # Basic smoke test make cluster-test-rollover # Segment rollover make cluster-test-resilience # Node failure recovery make cluster-test-recovery # Cluster restart persistence make cluster-test-stress # Concurrent writes make cluster-test-multi-topic # Multiple topics
- Write throughput: Single writer per segment (lease-based)
- Read throughput: Scales with replicas (sealed segments)
- Latency: ~1-2 RTT for forwarded ops + storage latency
- Consensus overhead: Metadata only (not data path)
- Segment rollover: ~1M entries default (~100MB depending on payload size)
Walrus includes a formal TLA+ specification of the distributed data plane that models segment-based sharding, lease-based write fencing, and cursor advancement across sealed segments.
Specification: distributed-walrus/spec/DistributedWalrus.tla
- Domain Consistency: Topic metadata, WAL entries, and reader cursors stay synchronized
- Single Writer per Segment: Only the designated leader can write to each segment
- No Writes Past Open Segment: Closed segments remain immutable after rollover
- Sealed Counts Stable: Entry counts for sealed segments match actual WAL contents
- Read Cursor Bounds: Cursors never exceed segment boundaries or entry counts
- Sequential Write Order: Entries within each segment maintain strict ordering
- Rollover Progress: Segments exceeding the entry threshold eventually roll over
- Read Progress: Available entries eventually get consumed by readers
The specification abstracts Raft consensus as a single authoritative metadata source and models Walrus storage as per-segment entry sequences. Model checking with TLC verifies correctness under concurrent operations
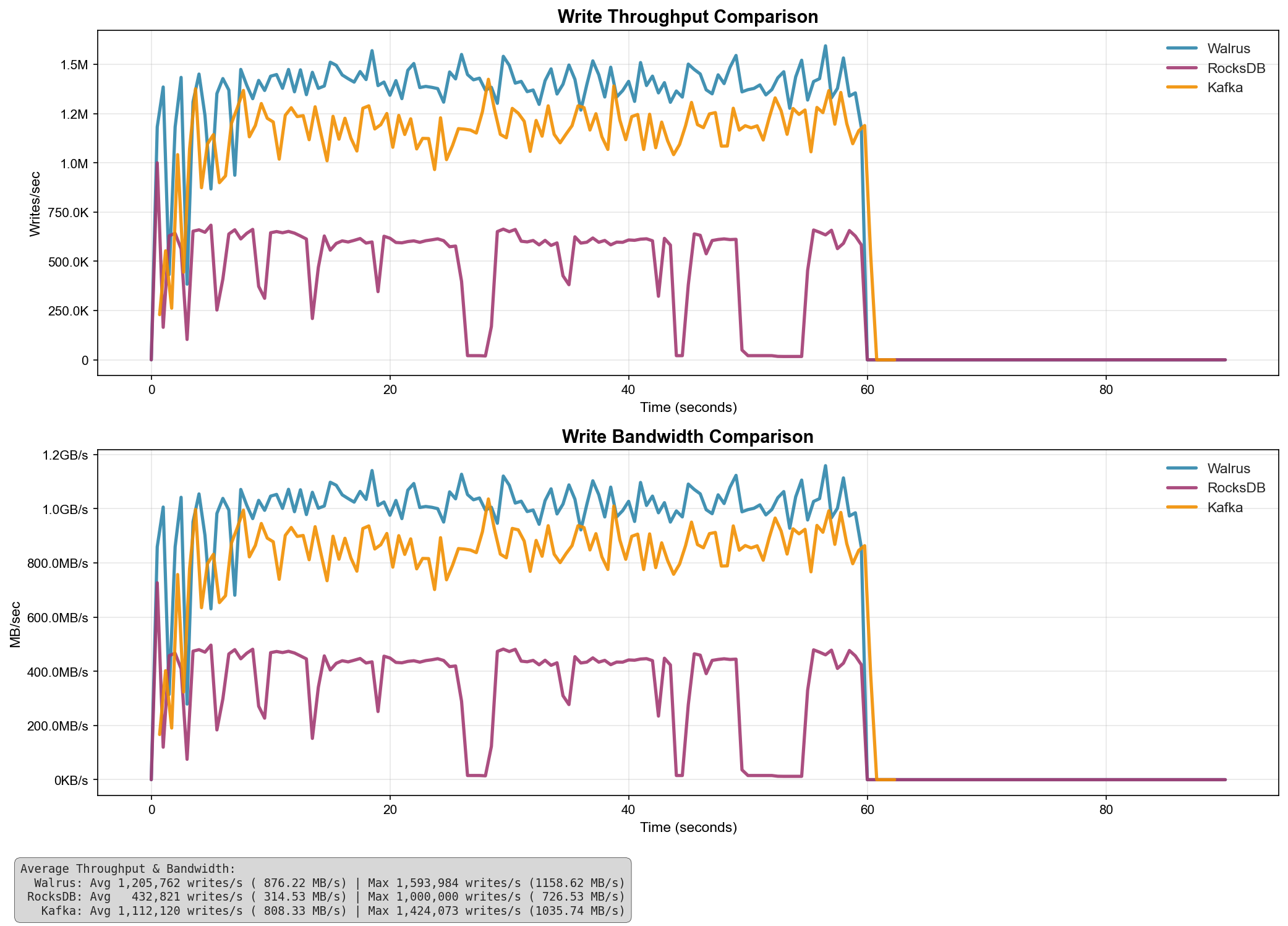
The underlying storage engine delivers exceptional performance:
| System | Avg Throughput (writes/s) | Avg Bandwidth (MB/s) | Max Throughput (writes/s) | Max Bandwidth (MB/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Walrus | 1,205,762 | 876.22 | 1,593,984 | 1,158.62 |
| Kafka | 1,112,120 | 808.33 | 1,424,073 | 1,035.74 |
| RocksDB | 432,821 | 314.53 | 1,000,000 | 726.53 |
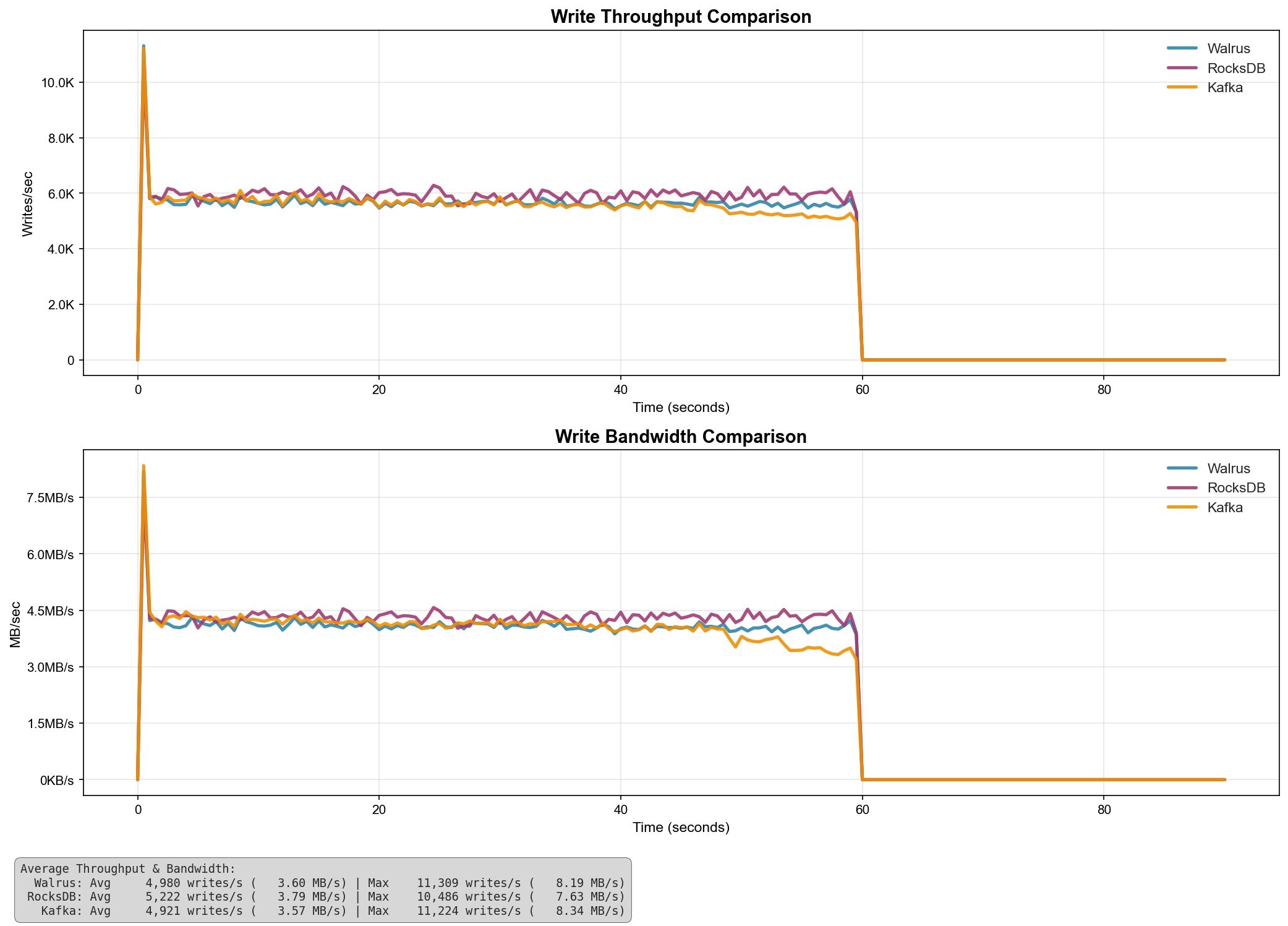
| System | Avg Throughput (writes/s) | Avg Bandwidth (MB/s) | Max Throughput (writes/s) | Max Bandwidth (MB/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RocksDB | 5,222 | 3.79 | 10,486 | 7.63 |
| Walrus | 4,980 | 3.60 | 11,389 | 8.19 |
| Kafka | 4,921 | 3.57 | 11,224 | 8.34 |
Benchmarks compare single Kafka broker (no replication, no networking overhead) and RocksDB's WAL against the legacy append_for_topic() endpoint using pwrite() syscalls (no io_uring batching).
- Architecture Deep Dive - Detailed component interactions, data flow diagrams, startup sequence, lease synchronization, rollover mechanics, and failure scenarios
- CLI Guide - Interactive CLI usage and commands
- System Documentation - Full system documentation
The core Walrus storage engine is also available as a standalone Rust library for embedded use cases:
[dependencies] walrus-rust = "0.2.0"
use walrus_rust::{Walrus, ReadConsistency}; // Create a new WAL instance let wal = Walrus::new()?; // Write data to a topic wal.append_for_topic("my-topic", b"Hello, Walrus!")?; // Read data from the topic if let Some(entry) = wal.read_next("my-topic", true)? { println!("Read: {:?}", String::from_utf8_lossy(&entry.data)); }
See the standalone library documentation for single node usage, configuration options, and API reference.
We welcome patches, check CONTRIBUTING.md for the workflow.
This project is licensed under the MIT License, see the LICENSE file for details.
- New: Distributed message streaming platform with Raft consensus
- New: Segment-based leadership rotation and load balancing
- New: Automatic rollover and lease-based write fencing
- New: TCP client protocol with simple text commands
- New: Interactive CLI for cluster interaction
- New: Comprehensive test suite for distributed scenarios
- New: Atomic batch write operations (
batch_append_for_topic) - New: Batch read operations (
batch_read_for_topic) - New: io_uring support for batch operations on Linux
- New: Dual storage backends (FD backend with pread/pwrite, mmap backend)
- New: Namespace isolation via
_for_keyconstructors - New:
FsyncSchedule::SyncEachandFsyncSchedule::NoFsyncmodes - Improved: Comprehensive documentation with architecture and design docs
- Improved: Enhanced benchmarking suite with batch operation benchmarks
- Fixed: Tail read offset tracking in concurrent scenarios
- Initial release
- Core WAL functionality
- Topic-based organization
- Configurable consistency modes
- Comprehensive benchmark suite
- Memory-mapped I/O implementation
- Persistent read offset tracking