Notes on cross-platform portability for scientific codes with legacy components.
Background
Most computational chemistry codes are developed on Linux. macOS shows up in CI matrices or in workshops, a conda-forge feedstock might cover the major platforms, but Windows tends to be tested last and debugged reluctantly 1. This is simply a consequence of the platforms available in most research groups and the priorities of the people writing the code 2.
I have been maintaining eOn 3 for a while now, through a GPR-dimer implementation (Goswami et al. 2025), an on-the-go variant (Goswami and Jónsson 2025), the NEB-MMF work (Goswami, Gunde, and Jónsson 2026), my thesis (Goswami 2025), and more recently the metatensor ecosystem integration (Bigi et al. 2026) 4 and an atomistic cookbook recipe for NEB with machine learning potentials. Along the way, and through contributions to chemfiles and asv, I have collected a tidy set of Windows-specific failure modes. Each has cost at least one CI cycle and occasionally an afternoon.
Reserved Filenames
Windows inherits from DOS a set of reserved device
names
that cannot be used as filenames, regardless of extension: CON, PRN,
AUX, NUL, COM1 through COM9, LPT1 through LPT9.
Case-insensitive, naturally. The Microsoft
documentation
is comprehensive, but in practice most people discover these constraints
from a CI failure rather than from reading the docs.
aux.py in asv_runner (2023)
When writing
asv_runner, the
runner component for the asv benchmarking tool, I had a perfectly
reasonable file called asv_runner/aux.py for auxiliary benchmark
configuration 5. On Linux, no problem. On Windows:
1ERROR: For req: asv-runner. The wheel has a file 'asv_runner/aux.py'
2trying to install outside the target directory
The wheel could not even be installed, let alone the repository
cloned 6. Since asv is used by NumPy, SciPy, and friends for
performance tracking, this surfaced quickly. The
fix was to
rename the file. The same issue appeared in
pypotlib shortly
after, because apparently one lesson is never enough.
CON.cpp in chemfiles (2026)
Three years later, while adding .con file support to
chemfiles, I named
the implementation files CON.hpp and CON.cpp after the format they
implement 7. CON is of course also a reserved device name.
The files were renamed to _CON.hpp and _CON.cpp. The list of
reserved names is short enough to memorize, but apparently long enough
to forget between projects. The divergence in kernel handling is shown
in Figure 1.
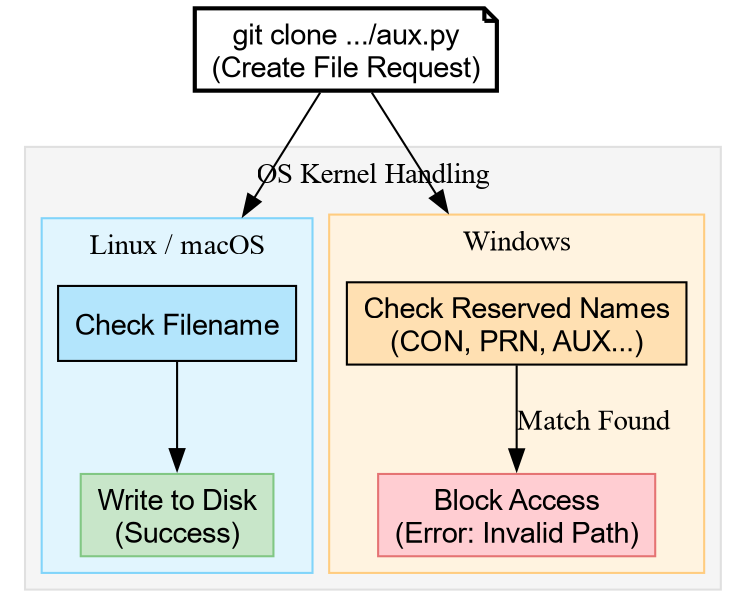
Figure 1: The OS kernel divergence: Windows blocks the request before it even reaches the disk if a reserved name is detected.
Stack Sizes and Legacy Fortran
The default stack size on Linux is typically 8 MB (ulimit -s). On
Windows, it is 1 MB. This is rarely a problem for modern C++ since
Eigen::MatrixXd and friends allocate on the heap, but it matters
enormously for legacy Fortran, where local arrays live on the stack by
default.
The GAGAFE Subroutine
The eOn code includes Embedded Atom Model potentials implemented in
Fortran 77. The core routine is called GAGAFE, and I rather enjoy
knowing where the name comes from 8:
GAGAFE stands for ‘group of atoms, group of atoms, force and energy’. In a system with two types of atoms, A and B, GAGAFE needed to be called three times, once for the A-A interactions, then for the B-B interactions and finally for the A-B interactions. This is coming from the code written in the H. C. Andersen group at Stanford (starting around 1980 when he wrote his famous paper on the velocity Verlet algorithm and the isobaric simulations with the extended Lagrangian). The code ran on a PDP-11 computer in combination with an array processor. I was a post-doc in the group 1986-1988 and kept this basic structure in the F77 code I wrote when I moved to Seattle in 1988.
– Hannes Jónsson (private communication)
There is something appealing about a subroutine name with a provenance older than most of its users. The code has been running continuously for over four decades, and it still works.. except on Windows, where the local arrays blow the stack.
The subroutine declares arrays dimensioned with compile-time constants:
1c parameters.cmn
2 parameter (MAXPRS = 200000)
3
4c gagafeDblexp.f
5 DIMENSION phi(MAXPRS), phivirst(MAXPRS)
6 DIMENSION RA1(MAXCOO), RA2(MAXCOO), FA1(MAXCOO), FA2(MAXCOO)
phi and phivirst alone consume around 3 MB. Including the remaining
arrays, the total stack footprint is roughly around 3.6 MB which is well
beyond the 1 MB Windows default. The client crashes on entry to the
potential routine with exit code 3221225725 (decimal), which is
0xC00000FD: STATUS_STACK_OVERFLOW (see Figure
2).
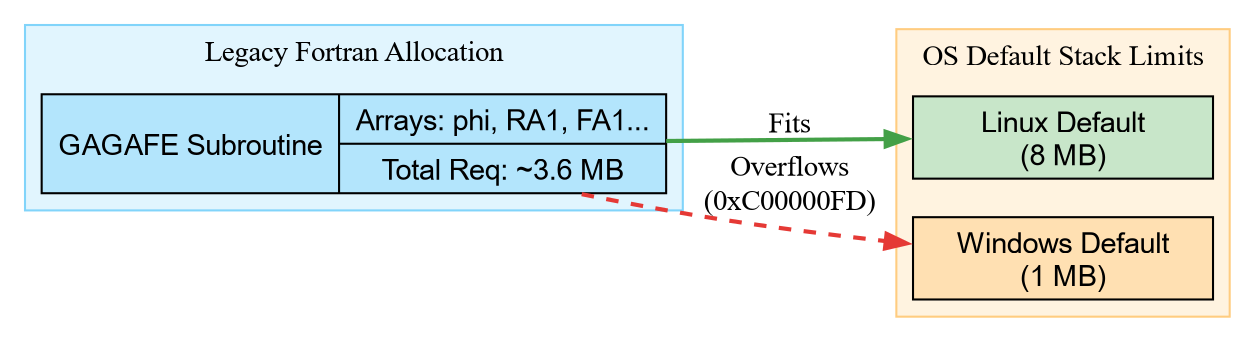
Figure 2: Visualizing the stack overflow: The legacy Fortran arrays fit comfortably within the Linux 8 MB default but exceed the Windows 1 MB limit.
The Fix
For Meson-based builds, the linker can request a larger stack:
1if is_windows
2 if is_mingw
3 _linkargs += ['-Wl,--stack,16777216'] # 16 MB
4 elif cppc.get_id() == 'msvc'
5 _linkargs += ['/STACK:16777216']
6 endif
7endif
The alternative is refactoring the Fortran to use ALLOCATABLE arrays
or COMMON blocks. For code with this kind of lineage, the linker flag
is less invasive. More on working with inherited Fortran in general can
be found in an earlier post.
Stdout Redirection and spdlog
The spdlog logging library provides stdout_color_sink_mt, which uses
ANSI escape codes on Linux and WriteConsole on Windows for colored
output. The catch: WriteConsole only
works when the output
handle is an actual console 9. When a parent process redirects
stdout to a file as the eOn Python server does for every client job,
WriteConsole fails silently.
The symptom is that the client produces no stdout whatsoever. stderr is empty. The exit code may or may not be informative depending on what else breaks downstream. The fix is to select the non-color sink:
1#ifdef _WIN32
2 auto console_sink =
3 std::make_shared<spdlog::sinks::stdout_sink_mt>();
4#else
5 auto console_sink =
6 std::make_shared<spdlog::sinks::stdout_color_sink_mt>();
7#endif
This took longer to diagnose than it should have, mostly because “no output” does not immediately suggest “color codes”, a mechanism detailed in Figure 3.
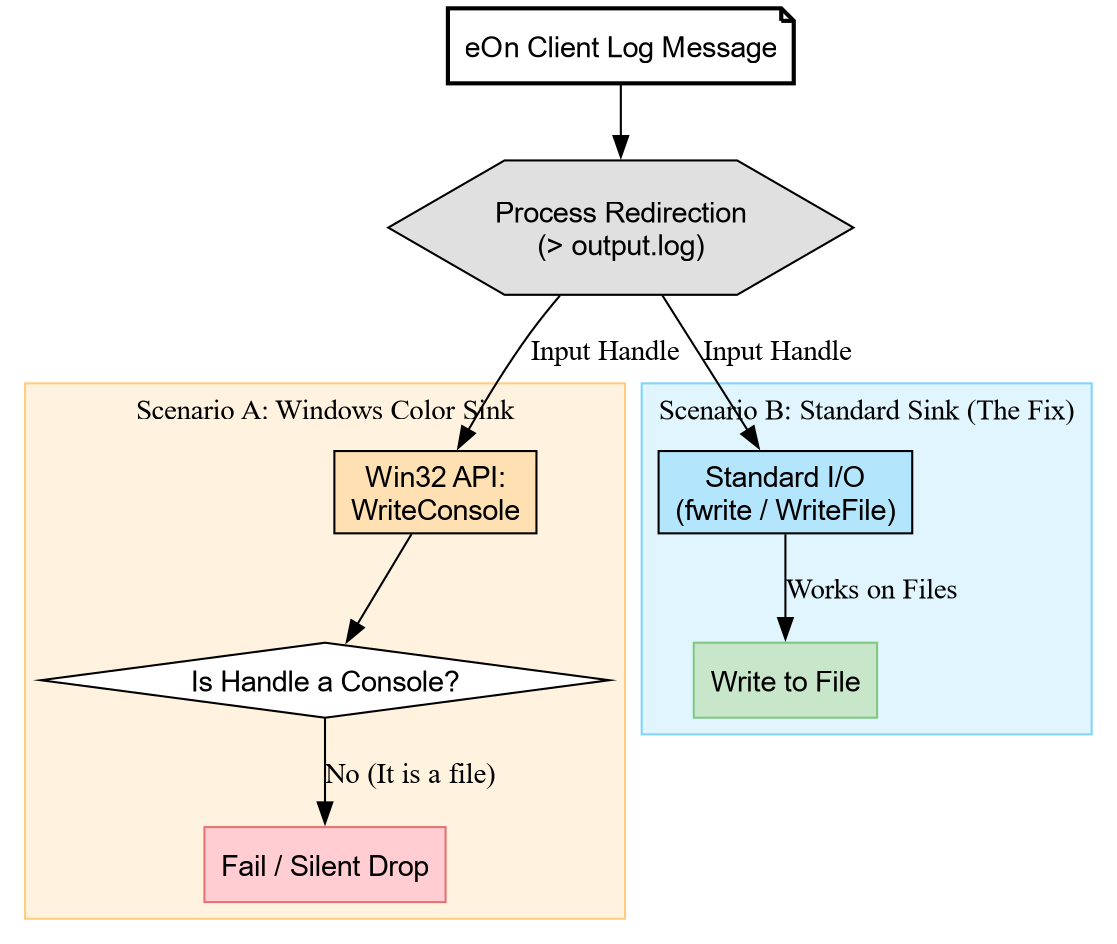
Figure 3: The silent failure mechanism: WriteConsole bypasses standard I/O and fails when the handle is a file, whereas standard sinks use file-compatible APIs.
None of these issues are particularly deep. The reserved filenames have
been documented since DOS. The 1 MB stack has been the default for
decades. The WriteConsole behavior has an open spdlog issue from
2020. The common thread is that they surface only when CI runs on a
platform the developer does not use daily, with error messages ranging
from cryptic (0xC00000FD) to absent.
The practical advice is simple: add Windows to the CI matrix early, and pay extra attention to legacy Fortran components where stack allocation is the default. And perhaps keep a list of DOS device names somewhere visible.
References
Bigi, Filippo, Joseph W. Abbott, Philip Loche, Arslan Mazitov, Davide Tisi, Marcel F. Langer, Alexander Goscinski, et al. 2026. “Metatensor and Metatomic : Foundational Libraries for Interoperable Atomistic Machine Learning.” Journal of Chemical Physics 164 (6): 64113. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0304911.
Goswami, Rohit. 2025. “Efficient Exploration of Chemical Kinetics.” October 24, 2025. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2510.21368.
Goswami, Rohit, Miha Gunde, and Hannes Jónsson. 2026. “Enhanced Climbing Image Nudged Elastic Band Method with Hessian Eigenmode Alignment.” January 22, 2026. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.12630.
Goswami, Rohit, and Hannes Jónsson. 2025. “Adaptive Pruning for Increased Robustness and Reduced Computational Overhead in Gaussian Process Accelerated Saddle Point Searches.” ChemPhysChem, November. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.202500730.
Goswami, Rohit, Maxim Masterov, Satish Kamath, Alejandro Pena-Torres, and Hannes Jónsson. 2025. “Efficient Implementation of Gaussian Process Regression Accelerated Saddle Point Searches with Application to Molecular Reactions.” Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation, July. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jctc.5c00866.
Series info
EON series
- Reconciling eOn for Academia and Open Source
- Windows Compatibility and Scientific Computing <-- You are here!
Series info
Fortran Frontiers: Bridging Legacy to Modernity series
- Handling Legacy Fortran Code
- Windows Compatibility and Scientific Computing <-- You are here!